The use of tense is inevitable in speaking and writing in the English language. If we don’t know the tense then we can’t write and speak English sentences completely. So it is important to know our tense first to write English sentences correctly.
So let’s learn about Tense in detail today.
What is Tense?
The word tense comes from the Latin Tempus or time. The word Tempus means time. That is the word tense means time. Tense is the main condition of learning and writing English correctly. So tense is called “Soul of the English Language”
So we can say the time of action of the verb is called Tense.
Read also: Best Advantages of a Student Laptop in 2022
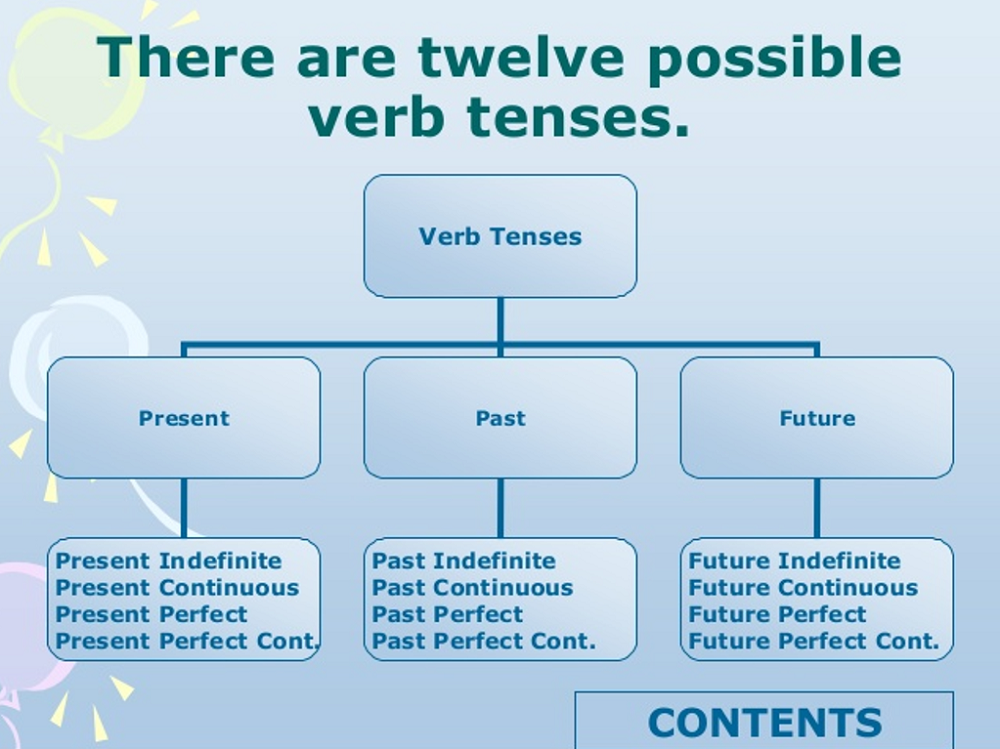
Kinds of Tense
There are mainly three types:
- Present Tense.
- Past Tense.
- Future Tense.
01. Present Tense:
When the work of the verb refers to Present time, it is called Present tense.
Example: He go to school.
Kinds of Present Tense.
There are mainly four types:
- Indefinite Tense
- Continuous Tense
- Perfect Tense
- Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Indefinite Tense:
Present Indefinite Tense denotes work in the present time or habitual truth or eternal truth.
Structure: Subject + Verb + (verb + s/es)
Example: We read books.
Present Continuous Tense: Present continuous tense is used when work is continued or going to be continued in near future.
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + (verb + ing )
Example: We are reading a book.
Present Perfect Tense: Present Perfect tense is used when the work has been done but result lasts.
Structure: Subject + has/have +(past participle of verb)
Example: He has studied for hours.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense: The Present Perfect continuous tense is used for work that began at some time in the past and is still continuing.
Structure: Subject + has been/ have been + (verb + ing )
Example: I have been doing this work for six days.
02. Past Tense:
When the work of the verb refers to past time, it is called past tense.
Kinds of Past Tense.
There are mainly four types:
- Indefinite Tense
- Continuous Tense
- Perfect Tense
- Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Indefinite Tense: Past Indefinite tense is used to denote work completed in the past or a past habit.
Structure: Subject + Past form of verb
Example: We did the work.
Past Continuous Tense: Past Continuous tense is used when the work was continued for some time in the past.
Structure: Subject + was/were + (verb + ing )
Example: We were playing cricket.
Past Perfect Tense: Past Perfect tense is used in the former work between two completed works of the past. A Simple past is used in the later action.
Structure: Subject + had + (past participle of verb)
Example: The train had started before I reached the station.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Past perfect continuous tense is used for work that began before a certain point in the past and continues up to that time
Structure: Subject + had been + (verb + Ing)
Example: Mr. Oaliur had been teaching there for five years.
03. Future Tense:
When the work of the verb refers to Future time, it is called future tense.
Kinds of Future Tense
There are mainly four types:
- Indefinite Tense
- Continuous Tense
- Perfect Tense
- Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Indefinite Tense: Future indefinite tense is used when work will be done or will happen in the future.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + verb
Example: We shall go to school.
Future Continuous Tense: Future continuous tense is used when work is thought to be going on in the future.
Structure: Subject + shall be/will be + (verb + ing)
Example: We shall be doing the work.
Future Perfect Tense: The Future perfect tense is used to indicate the completion of work by a certain time in the future.
Structure: Subject + shall have/ will have + (past participle of verb)
Example: I shall have done the work before my father comes.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense: Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used when the doer will have been doing the work by a certain future time.
Structure: Subject + shall have been /will have been + (verb + ing)
Example: By next July we shall have been living here for five years.




1 Comment
Reading your article helped me a lot and I agree with you. But I still have some doubts, can you clarify for me? I’ll keep an eye out for your answers.